이번에 6월 예제문제가 변경되었는데요.
2유형도 풀어봤습니다.
빅데이터 분석기사 2유형
데이터는 아래 형태인데요. 환불금액에 빵꾸가 있네요. 전처리가 필요합니다.
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 회원ID 3500 non-null int64
1 총구매액 3500 non-null int64
2 최대구매액 3500 non-null int64
3 환불금액 1200 non-null float64
4 주구매상품 3500 non-null object
5 주구매지점 3500 non-null object
6 방문일수 3500 non-null int64
7 방문당구매건수 3500 non-null float64
8 주말방문비율 3500 non-null float64
9 구매주기 3500 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(5), object(2)
object는 LabelEncoder로 전처리가 필요합니다.
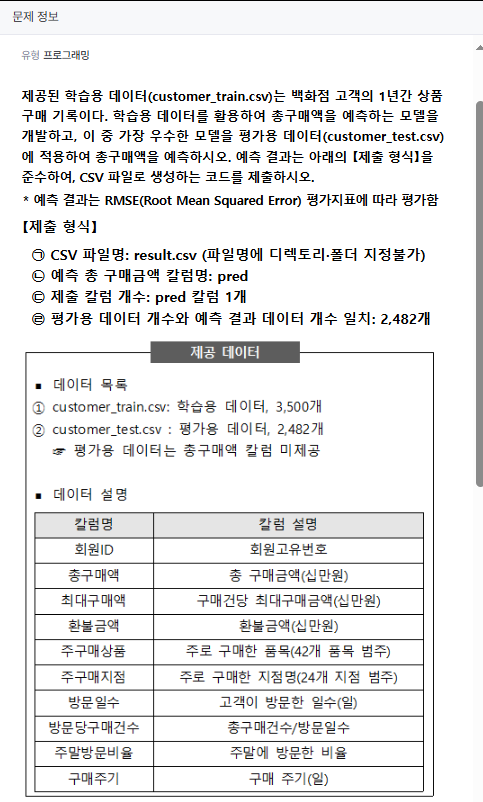
2유형은 백화점 고객의 1년간 상품 구매 기록을 보고 회귀 문제입니다.
회귀문제는 RandomForestRegressor이라는 것을 명심하고 문제를 풉니다.
# 출력을 원하실 경우 print() 함수 활용
# 예시) print(df.head())
# getcwd(), chdir() 등 작업 폴더 설정 불필요
# 파일 경로 상 내부 드라이브 경로(C: 등) 접근 불가
import pandas as pd
train = pd.read_csv("data/customer_train.csv")
test = pd.read_csv("data/customer_test.csv")
# 사용자 코딩
# 답안 제출 참고
# 아래 코드는 예시이며 변수명 등 개인별로 변경하여 활용
# pd.DataFrame변수.to_csv("result.csv", index=False)
import numpy as np
#데이터 확인
#print(train.info()) #주구매상품, 주구매지점 (라벨인코딩) / 환불금액 결측값 처리
#print(train.head())
#print(test.info())
#print(test.head())
#데이터 전처리
train['환불금액'] = train['환불금액'].fillna(train['환불금액'].mode()[0])
test['환불금액'] = test['환불금액'].fillna(test['환불금액'].mode()[0])
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
#항목 확인)
set(train['주구매상품'] - test['주구매상품'])
train['주구매상품'] = le.fit_transform(train['주구매상품'])
test['주구매상품'] = le.transform(test['주구매상품'])
train['주구매지점'] = le.fit_transform(train['주구매지점'])
test['주구매지점'] = le.transform(test['주구매지점'])
#from sklearn.preprocessing import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#print(help(sklearn))
X = train.drop(columns=['총구매액','회원ID'])
y = train['총구매액']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=10)
X_train.info()
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
rfr = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=500, max_depth=30, random_state=10)
rfr.fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = rfr.predict(X_test)
from sklearn.metrics import root_mean_squared_error
import sklearn
#print(dir(sklearn.metrics))
rmse = root_mean_squared_error(y_test, pred)
print(rmse)
test_X = test.drop(columns = '회원ID')
pred2 = rfr.predict(test_X)
print(pred2)
pd.DataFrame({'pred':pred2}).to_csv('result.csv', index=False)
print(pd.read_csv('result.csv'))
모르면 dir로 metrics에 머가 있는지 확인해봅니다.
| ['ConfusionMatrixDisplay', 'DetCurveDisplay', 'DistanceMetric', 'PrecisionRecallDisplay', 'PredictionErrorDisplay', 'RocCurveDisplay', '__all__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__', '__spec__', '_base', '_classification', '_dist_metrics', '_pairwise_distances_reduction', '_pairwise_fast', '_plot', '_ranking', '_regression', '_scorer', 'accuracy_score', 'adjusted_mutual_info_score', 'adjusted_rand_score', 'auc', 'average_precision_score', 'balanced_accuracy_score', 'brier_score_loss', 'calinski_harabasz_score', 'check_scoring', 'class_likelihood_ratios', 'classification_report', 'cluster', 'cohen_kappa_score', 'completeness_score', 'confusion_matrix', 'consensus_score', 'coverage_error', 'd2_absolute_error_score', 'd2_log_loss_score', 'd2_pinball_score', 'd2_tweedie_score', 'davies_bouldin_score', 'dcg_score', 'det_curve', 'euclidean_distances', 'explained_variance_score', 'f1_score', 'fbeta_score', 'fowlkes_mallows_score', 'get_scorer', 'get_scorer_names', 'hamming_loss', 'hinge_loss', 'homogeneity_completeness_v_measure', 'homogeneity_score', 'jaccard_score', 'label_ranking_average_precision_score', 'label_ranking_loss', 'log_loss', 'make_scorer', 'matthews_corrcoef', 'max_error', 'mean_absolute_error', 'mean_absolute_percentage_error', 'mean_gamma_deviance', 'mean_pinball_loss', 'mean_poisson_deviance', 'mean_squared_error', 'mean_squared_log_error', 'mean_tweedie_deviance', 'median_absolute_error', 'multilabel_confusion_matrix', 'mutual_info_score', 'nan_euclidean_distances', 'ndcg_score', 'normalized_mutual_info_score', 'pair_confusion_matrix', 'pairwise', 'pairwise_distances', 'pairwise_distances_argmin', 'pairwise_distances_argmin_min', 'pairwise_distances_chunked', 'pairwise_kernels', 'precision_recall_curve', 'precision_recall_fscore_support', 'precision_score', 'r2_score', 'rand_score', 'recall_score', 'roc_auc_score', 'roc_curve', 'root_mean_squared_error', 'root_mean_squared_log_error', 'silhouette_samples', 'silhouette_score', 'top_k_accuracy_score', 'v_measure_score', 'zero_one_loss'] |
'Programming > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 파이썬 이미지 인식 연습 (0) | 2026.01.01 |
|---|---|
| 빅데이터 분석기사 실기 3유형 (0) | 2025.06.11 |
| 빅데이터 분석기사 6월 실기 1유형 (0) | 2025.06.11 |
| 파이썬 pyinstaller 용량 줄이기 (0) | 2025.03.05 |
| CloudScraper로 크롤링 우회하기 (0) | 2024.11.21 |